Understanding Request Fulfillment
When access requests are approved through EmpowerID's approval workflows, the system must execute the approved actions—provisioning accounts, adding group memberships, assigning roles, or other operations. This article explains the fulfillment architecture that processes approved requests and ensures each action completes successfully at scale.
The Request Pipeline
Access requests in EmpowerID flow through a multi-stage pipeline from initiation to completion. Understanding this pipeline clarifies where fulfillment occurs and how it integrates with approval processes.
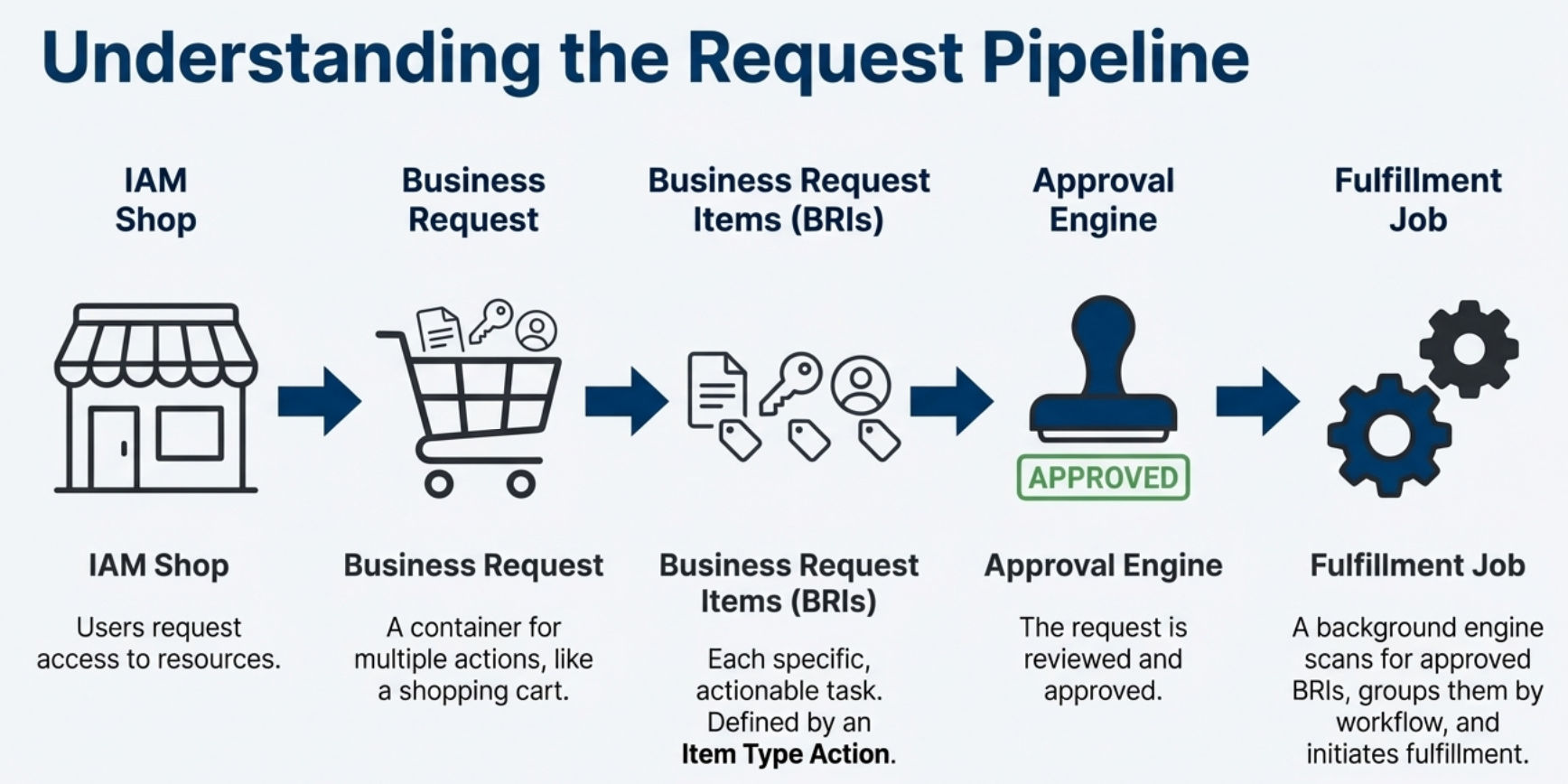
IAM Shop: Users request access to resources by adding items to a shopping cart and submitting their order.
Business Request: The submitted order becomes a Business Request—a container that groups multiple requested actions together.
Business Request Items (BRIs): Each specific action within a Business Request becomes a Business Request Item. A single request might contain multiple BRIs, such as "Add Account to Group A" and "Assign Azure License B."
Approval Engine: The Approval Engine routes BRIs through configured approval workflows based on policies and determines which items require human approval.
Fulfillment Job: Once approved, the Fulfillment Job identifies ready-to-execute BRIs and initiates their processing.
Execution: Fulfillment workflows perform the actual operations—creating accounts, modifying permissions, or executing other defined actions.
Business Request Items
Business Request Items represent individual, actionable tasks within a Business Request. Each BRI defines:
- Target Resource: The resource being acted upon (account, group, role, application)
- Action Type: The operation to perform (add, remove, modify, provision)
- Requester Context: Who initiated the request and for whom
- Approval Status: Current state in the approval workflow
BRIs provide granular tracking for complex requests. When a user requests membership in five groups, EmpowerID creates five separate BRIs—each with independent approval requirements and fulfillment status. This granularity enables precise monitoring, auditing, and reporting at the individual action level.
The Fulfillment Job
The Business Request Item Fulfillment Job monitors approved BRIs and orchestrates their execution. This background process runs continuously, scanning for BRIs that have completed all required approval steps and are ready for fulfillment.
The Fulfillment Job serves as the automation engine that processes approved requests without manual intervention. It ensures approved actions execute promptly and handles large volumes of requests efficiently by processing items in bulk.
Fulfillment Routing
The Fulfillment Job routes approved BRIs to execution workflows based on their Item Type Action configuration. Each Item Type Action in EmpowerID specifies which workflow should fulfill that particular operation.
For example:
- "Add Account to Group" might route to a specific group membership workflow
- "Provision Azure License" routes to a license assignment workflow
- "Create Mailbox" routes to an Exchange provisioning workflow
This routing mechanism allows different types of requests to follow appropriate fulfillment logic while maintaining a unified request processing pipeline.
The Four-Stage Fulfillment Pattern
Fulfillment workflows in EmpowerID follow a standardized four-stage execution pattern. This architecture ensures consistent, reliable processing regardless of the specific operation being performed.
Stage 1: Validate
The workflow verifies that incoming BRIs are valid, untampered, and ready for processing. Validation confirms that:
- BRI data is complete and correctly structured
- Referenced resources still exist in the system
- No concurrent operations have invalidated the request
- The BRI has not already been processed
Invalid or incomplete BRIs are flagged and do not proceed to execution.
Stage 2: Prepare Inputs
The workflow extracts data from BRIs and transforms it into the format required for the bulk operation. This stage:
- Retrieves target resource information (account identifiers, group names, etc.)
- Filters data based on current resource state
- Structures data for efficient bulk processing
- Creates a mapping between each resource and its originating BRI
Preparation ensures that bulk operations receive properly formatted data and that the workflow can correlate execution results back to specific BRIs.
Stage 3: Execute Operation
The workflow performs the actual bulk operation. This is where accounts are modified, permissions are granted, resources are provisioned, or other system changes occur.
Bulk operations process multiple items simultaneously, dramatically improving performance compared to processing each item individually. For example, adding 100 accounts to a group executes as a single operation rather than 100 separate operations.
The execution stage returns a collection of results indicating success or failure for each processed item.
Stage 4: Update Status
The workflow maps execution results back to the originating BRIs and updates their fulfillment status. This stage:
- Correlates each result with its source BRI using the mapping created in Stage 2
- Sets BRI status to Success or Failure based on execution outcome
- Records error details for failed operations
- Commits all status updates in a single transaction
Status updates ensure that Business Request tracking reflects the actual outcome of fulfillment operations. Users and approvers can see which items succeeded and which require attention.
Mapping Results to Business Request Items
A critical aspect of the fulfillment architecture is maintaining the link between bulk operation results and individual BRIs. Since bulk operations process multiple items together, the system must track which operation result corresponds to which Business Request Item.
The fulfillment workflow creates this connection during the Prepare stage. As the workflow gathers resources for bulk processing, it records which BRI initiated each action. When the bulk operation completes and returns results, the workflow uses this record to match each result back to its original BRI and update the status accordingly.
For example, if 50 users request membership in the same group, the fulfillment workflow processes all 50 as a single bulk operation. The workflow maintains a record linking each of the 50 accounts to their specific BRI. When the operation completes, the workflow can report that "BRI for User 1: Success, BRI for User 2: Success, BRI for User 3: Failed" even though all 50 were processed together.
This mapping mechanism enables precise status reporting even when processing hundreds or thousands of BRIs in a single bulk operation.
Bulk Processing and Scale
The fulfillment architecture emphasizes bulk operations for scalability. Rather than processing requests one at a time, the system groups similar operations together and executes them as batches.
For example, if 50 users request membership in the same group, the fulfillment workflow:
- Validates all 50 BRIs
- Prepares a single list of 50 accounts
- Executes one bulk "Add Accounts to Group" operation
- Maps the 50 results back to their respective BRIs
- Updates all 50 BRI statuses
This approach dramatically reduces the time and system resources required to fulfill large volumes of requests. Organizations with thousands of daily access requests can process them efficiently without creating system bottlenecks.
Bulk processing delivers significant performance improvements. An operation that might take 100 separate database calls when processing items individually requires only 1-2 calls when processed in bulk. This reduction in overhead allows the system to handle enterprise-scale request volumes.
Fulfillment Workflows
Multiple types of workflows can fulfill approved requests in EmpowerID:
No Code Flows: Visual workflows built without writing code. Administrators configure fulfillment logic through the EmpowerID interface, defining which operations to execute and how to handle results. No Code Flows are documented in detail in the No Code Flows section.
Custom Workflows: Developers can create specialized fulfillment workflows in Visual Studio for complex requirements that extend beyond No Code Flow capabilities.
Permanent Workflows: Background workflows that continuously monitor and fulfill specific types of requests based on policy-driven automation.
All fulfillment workflow types integrate with the same Business Request Item Fulfillment Job and follow the same four-stage execution pattern, ensuring consistent behavior regardless of implementation method.
Status Tracking and Monitoring
Throughout the fulfillment process, EmpowerID maintains detailed status information for each BRI. Status values include:
- Pending: Awaiting approval or fulfillment
- In Progress: Currently being processed
- Success: Fulfillment completed successfully
- Failed: Fulfillment encountered an error
- Skipped: Item bypassed based on policy or conditions
These statuses appear in the My Tasks interface, allowing requesters and approvers to monitor progress. Detailed logs capture execution information for troubleshooting failed operations.
Integration with Approval Workflows
The fulfillment architecture integrates seamlessly with EmpowerID's approval workflows. The Approval Engine determines which BRIs require human approval and routes them through appropriate approval steps. Once approved, these BRIs automatically become available for the Fulfillment Job to process.
For requests that do not require approval, the fulfillment process begins immediately. The system evaluates RBAC permissions and proceeds directly to fulfillment for authorized operations.
This integration ensures that all access requests—whether requiring approval or not—follow the same execution path once authorized, providing consistent processing and audit trails.
Key Principles
Separation of Concerns: The fulfillment architecture separates approval logic from execution logic. Approval workflows determine whether an action should occur; fulfillment workflows determine how to execute it.
Consistent Execution Pattern: The four-stage pattern (Validate → Prepare → Execute → Update) provides a reliable framework for building fulfillment workflows that handle any operation type.
Bulk-First Processing: Grouping similar operations and processing them together delivers the performance required for enterprise-scale access management.
Granular Tracking: Individual BRI status tracking enables precise monitoring and reporting, even when processing thousands of requests simultaneously.
Workflow Flexibility: Multiple workflow implementation options (No Code, custom, permanent) support diverse organizational requirements while maintaining architectural consistency.
This fulfillment architecture enables EmpowerID to process access requests reliably at scale while providing visibility into the status and outcome of each individual action.